G#sus4 Guitar Chord | Play, Hear and Practice Interactively
Want a structured chord roadmap instead of jumping between pages?
Download the step-by-step Guitar Chord Ebook
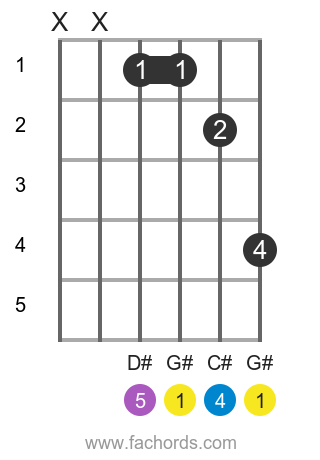
The G# sus4 chord, part of the suspended chords family, is built from the notes G#, C#, and D#, corresponding to the intervals 1 (Root), 4 (Perfect Fourth), and 5 (Perfect Fifth). Use the interactive fretboard tool at the top of this page to visualize fingerings, listen to the chord played as a strum or arpeggio, and get instant feedback on your playing with the real-time microphone.
Suspended chords, like the G# sus4, are unique because they replace the third with a fourth or a second, creating an unresolved sound. For a deeper dive into this unique chord type, explore our guide to Suspended Chords. Understanding how chords are constructed by stacking intervals is key – our Chord Construction tutorial provides a solid foundation.
Further down, you'll find detailed G# sus4 chord diagrams, ranked from easiest open positions to more challenging movable shapes. We'll also cover relevant music theory, popular songs that feature the G# sus4, and the musical keys where it often appears. Before you dive into the diagrams, make sure to spend some time with the interactive tool above. It's the fastest way to hear how the chord sounds, practice your finger placement with the mic feedback, and truly integrate it into your playing.
Notes of the G# sus4 chord:
Chord Structure:
G# Suspended Fourth Guitar Chord Shapes
Position 1
Movable
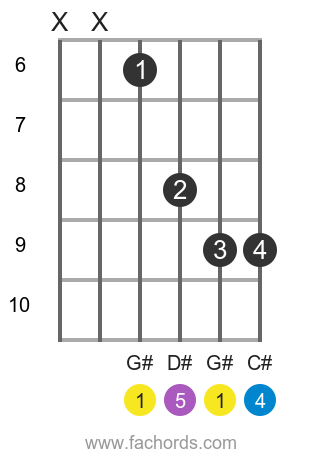
Position 2
Barre
Movable

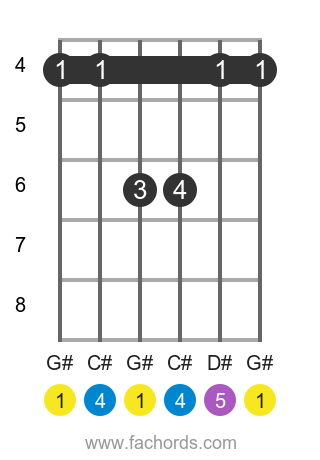
Position 3
Barre
Movable
 Find more shapes in our all guitar chords online library. If you
prefer a printable pdf, download
the Free Guitar Chords Chart Pdf
Find more shapes in our all guitar chords online library. If you
prefer a printable pdf, download
the Free Guitar Chords Chart Pdf
You can also use this accessible G#sus4 chord page, with written diagram instructions and screen-reader support for blind users.
FAQ
What notes make up the G# sus4 chord?
The G# sus4 chord is composed of three specific notes: G#, C#, and D#. These notes give the chord its distinct sound and structure on the guitar.
What are the characteristic intervals of a G# sus4 chord?
The G# sus4 chord is built using specific intervals relative to its root note, G#. These intervals are the 1 (Root), the 4 (Perfect Fourth), and the 5 (Perfect Fifth).
What makes the G# sus4 a 'suspended' chord?
The G# sus4 is classified as a suspended chord because it does not contain a major or minor third. Instead, the third interval is replaced by a perfect fourth, which is a defining characteristic of sus4 chords.
Why does the G# sus4 chord have an 'unresolved' sound?
The unresolved sound of the G# sus4 chord stems from the absence of the major or minor third. The presence of the perfect fourth interval instead of the third creates a harmonic tension that often suggests a desire to resolve to a more stable chord.
How is the G# sus4 chord typically used in a musical context?
The G# sus4 chord is versatile and can add depth and complexity to music. A common application is to use it as a substitute for a G# major chord, for example, as the '1' chord in a 1-4-5 progression, which introduces an interesting and unique twist to the harmony.
What is the main difference between a G# sus4 chord and a standard G# major chord?
The fundamental difference lies in their internal structure: a G# major chord contains a major third, while a G# sus4 chord replaces that major third with a perfect fourth. This substitution removes the definitive major quality, giving the G# sus4 its open, 'suspended,' and unresolved character.
